BLUETOOTH (IEEE 802.15.1)
Protocol for PAN communication, based on 2.4 frequencies band,it aims to the following goals:
- low cost device
- low distance communication
- voice and data management
This comes with the cost of lower bandwidth so lower data transfer rate
PROTOCOL STACK
Bluetooth is a complex stack of protocols at different layer and devices can implement only a subset of functionality and not all
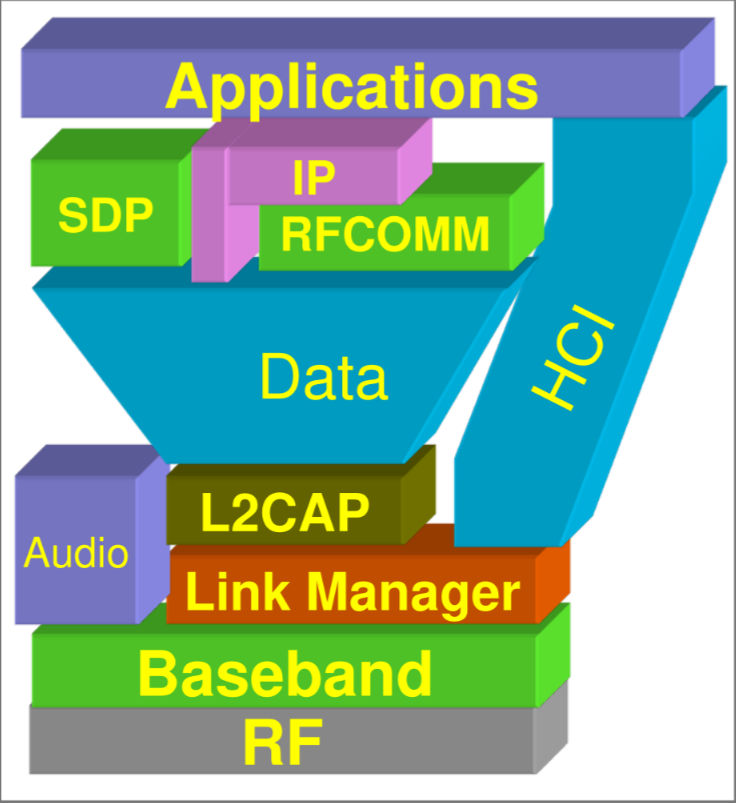
ARCHITECTURE
Bluetooth architecture is called PICO-NET where a node plays the role of master and manages the communication with the other nodes and between nodes
flowchart TD A[MASTER] B[node] C[node] D[node] A --> B & D & C
Where:
- there is always a unique master node
- maximum of 7 active nodes
- communication happens on a single channel using frequency hopping
PREPARATION PHASE
In order to communicate 2 nodes need to complete a preparation phase in order to construct the topology, this phase is spit in 2 sub-phases:
- INQUIRY PHASE a node start the discovery of nearby nodes and become the master
- PAGING PHASE master establish a bidirectional communication channel in frequency hopping with the slave nodes
flowchart TD subgraph inquiry mode A((master)) end subgraph inquiry scan mode B((slave1)) C((slave2)) D((slave3)) end subgraph nodes out of range E((node1)) F((node2)) end A --> B A --> C A --> D
One of the main constraint of Bluetooth communication is that nodes need to have their clock synchronized, this is done by imposing the master clock to the slaves that adapts their clocks
COMMUNICATION WITH MASTER
Time is divided by time slots in which only 2 nodes can communicate This is done in order to avoid collisions
The master decide which node can communicate, the master can communicate in all the odd slots
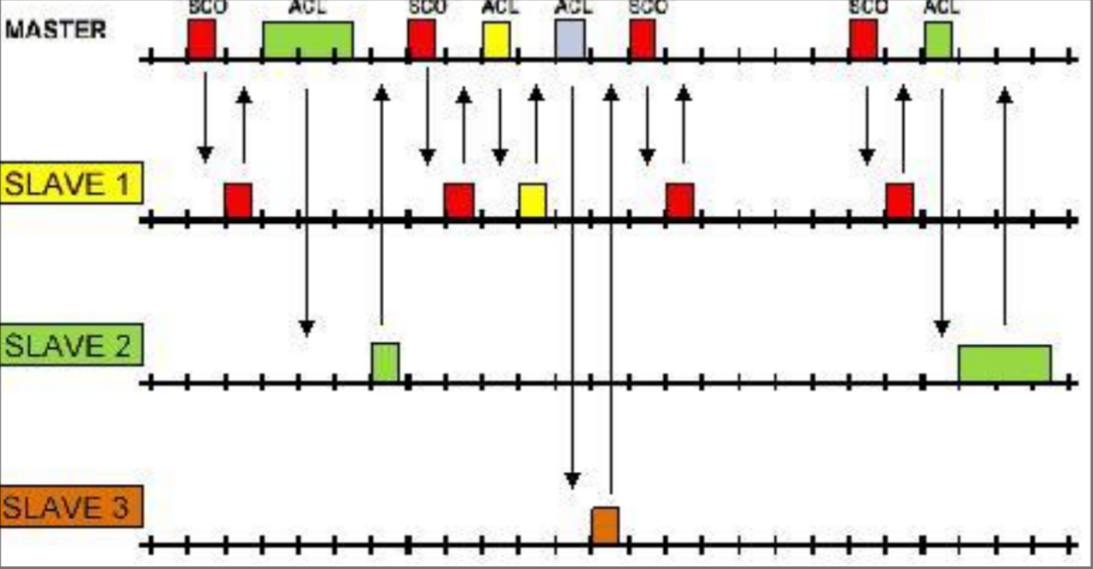
SCO CHANNELS
SCO packets are sent in pre-allocated time slots, in order to guarantee a fixed bandwidth (must have for audio streaming applications)
In order to avoid the consumption of all time slots the master can establish 3 SCO channels at the same time
In this mode re transmissions are not allowed
ACL CHANNELS
ACL packets are best effort communication with no guaranteed bandwidth this allow for higher bandwidth, it also support asymmetric bandwidth allocation for the 2 directions
In this connection types the slave can transmit only if in the previous time slot has received a packet from the master
In this mode retransmissions are allowed
MULTI HOP COMMUNICATION (SCATTER NET)
Bluetooth supports communication between PICO-NETs if the range allows it
flowchart TD subgraph piconet1 A[1] B[2] C[3] end subgraph piconet2 D[4] E[5] F[6] end A <--> B & C D <--> E & F A <--> D
In this configuration a node for each net is selected as the gateway that can forward traffic to the other net. This is a possibility allowed by the protocol but it’s not implemented for performance reasons
SERVICE DISCOVERY PROTOCOL
Bluetooth has a discovery protocol in order to identify nodes in the range, this allows also to discover what service the device can offer
BLUETOOTH LOW ENERGY BLE
Improvements in energy consumption with the same performances different set of channels (40 2-MHz channels). Within a channel, data is transmitted using Gaussian frequency shift modulation. Bitrate is 1 Mbit/s, and the maximum transmit power is 10 mW
The main difference is in the protocol of discovery and advertisement on the availability for piconets which is based on discovery packet broadcasting
All BLE devices implements the generic attribute (GATT) profile
BLUETOOTH VS WIFI
| WIFI | BLUETOOTH |
|---|---|
| multi node communication | point to point communication only |
| no discovery needed | need of discovery phase in order to communicate with a node |
| communication can be done in broadcast mode | no efficient broadcast support |