BASE TECHNIQUES
DISTANCE COMPUTATION
In order to compute position several methods relies on computing distance between nodes, several approaches are available
-
time of arrival (ToA) , the distance is computed as
-
Received signal strength indication (RSSI) , the distance is computed by the received signal strength
POSITION COMPUTATION
position can be computed using several geometrical and non geometrical approaches:
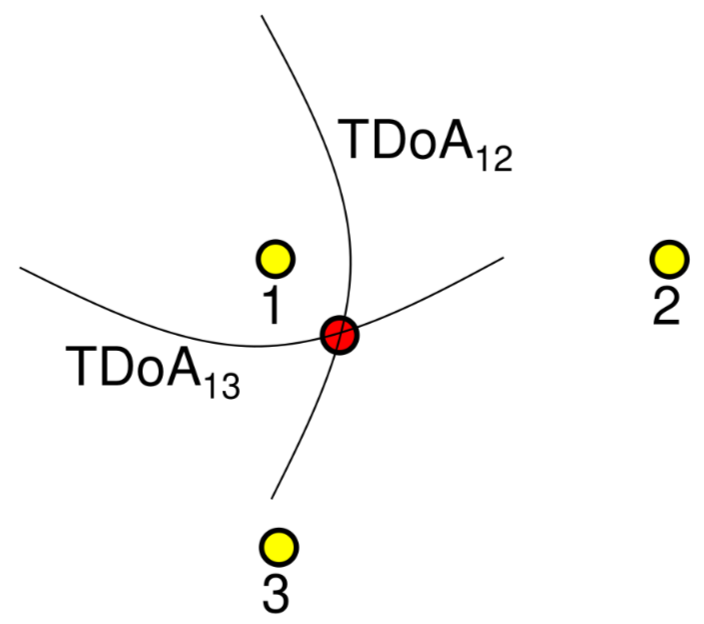
Time difference of arrival (TDoA)
given 2 reference points TDoA is the set of points where
LATERATION
the position is determined by computing distances from 3 reference points
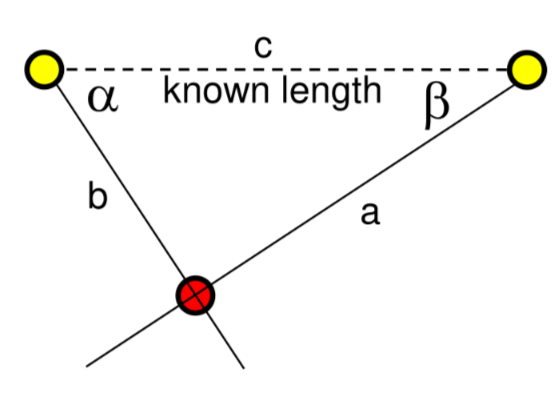
ANGULATION
based on the fact that the distance between 2 reference points is known, it computes the position using the Carnot’s theorem:
PROXIMITY
The current position is determined by the closest reference point to the node, ToA or RSSI can be deployed
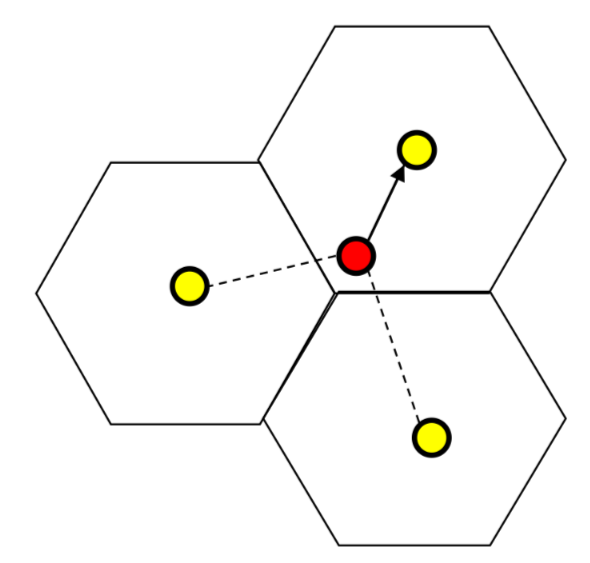
SCENE ANALYSIS
This is a statistical approach based on the knowledge of the deployment environment and of a dataset of observations made of it (e.g. RSSI)
this approach is composed by two phases
- Preliminary phase data are collected by observation and monitoring of the environment
- Operational phase environment observation are compared to the collected data to estimate position
ERROR SOURCES
Several things can cause error in position measurement such as:
- Non Line of Sight (NLOS) a node is not in direct visibility
- clock skew clock are not synchronized
- fading due to obstacle presence